9
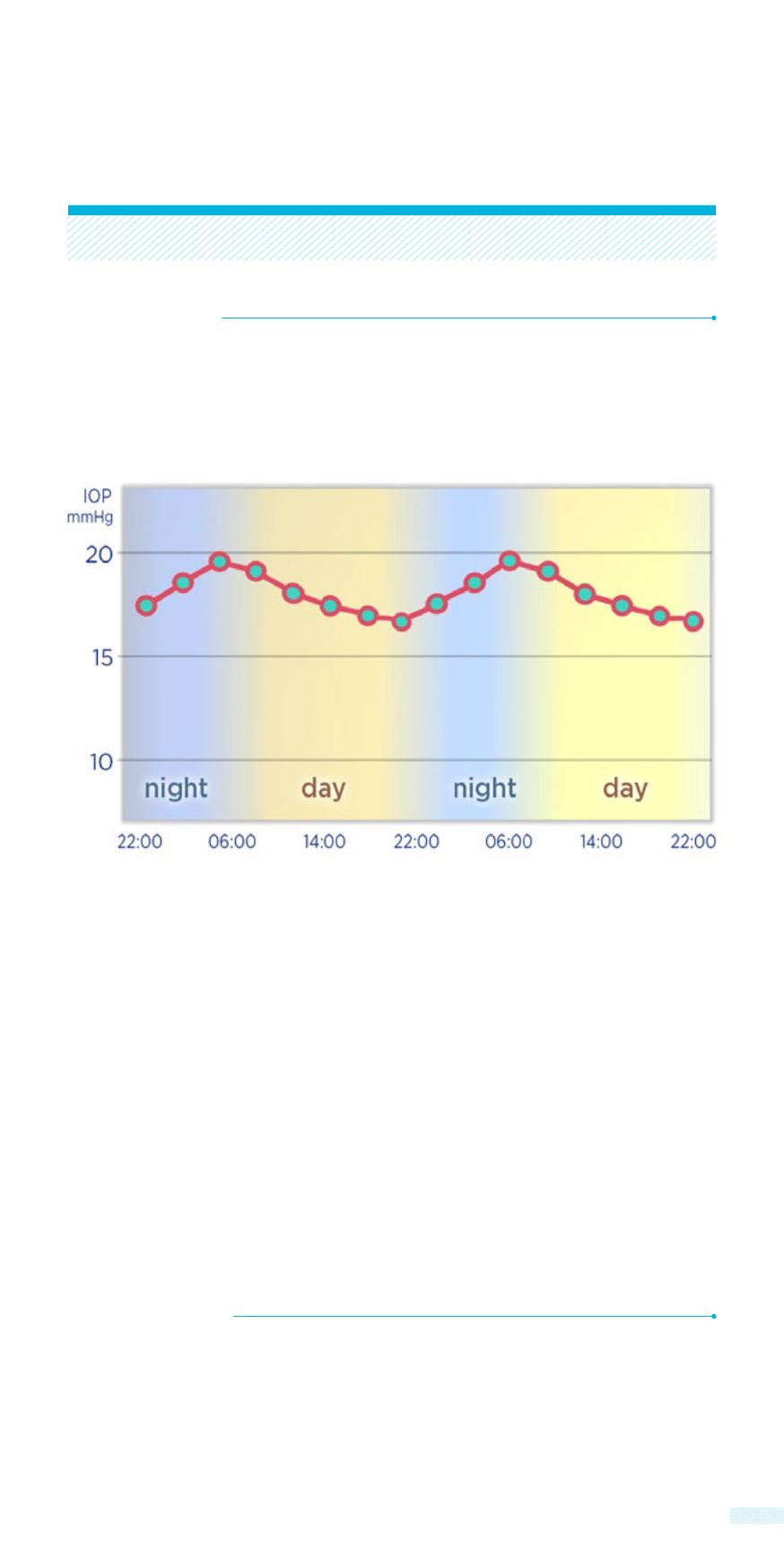
This is the term used for the measurement of intraocular pressure. It
is performed in each eye separately and often in different hours of
the day to record a 24h fluctuation. Intraocular pressure is commonly
highest in the early hours of the morning and then gradually
decreases to rise again the next morning. That is why most anti-
glaucoma drops are instilled in the evening, to prevent the morning
rise.
22 mmHg is considered the upper normal limit for intraocular
pressure.
Intraocular pressure alone does not set the diagnosis of
glaucoma. There has to be taken into consideration all clinical and
evaluation data, in order to come to a decision whether or not a
person really needs therapy. Furthermore, as has already been
mentioned, pressure within normal limits is not necessarily safe and
does not exclude the possibility of optic nerve damage.
Tonometry
Diagnostic evaluation of
glaucoma
Gonioscopy
Gonioscopy is the direct analysis of the irrigating angle with the
use of a special contact lens. With this examination, the angle can
be examined with no doubt as to its width and any pathological
findings, that can cause blockage to be revealed. There are different


